Week 1 L3: Discrete time Signal Synthesis and capture
Contents
Introduction
Mathematical description of and MATLAB creation of discrete time
- delta function
- unit step
- unit exponential
- simple sinusoid


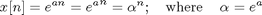
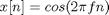
Sinusoid
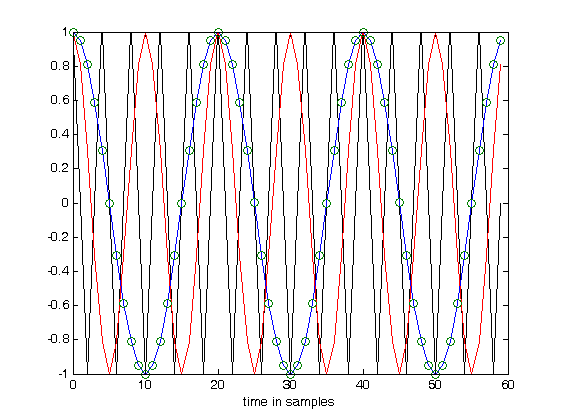
figure(1) N=60; % Number of samlpes n=0:N-1; % Set up sample axis x=cos(2*pi*.25*n) plot(n,x,'k') hold on x=cos(2*pi*.1*n); plot(n,x,'r') x=cos(2*pi*.05*n); plot(n,x,'b') xlabel('time in samples') plot(n,x,n,x,'o') hold off
x =
Columns 1 through 6
1.0000 0.0000 -1.0000 -0.0000 1.0000 0.0000
Columns 7 through 12
-1.0000 -0.0000 1.0000 0.0000 -1.0000 -0.0000
Columns 13 through 18
1.0000 -0.0000 -1.0000 -0.0000 1.0000 -0.0000
Columns 19 through 24
-1.0000 -0.0000 1.0000 -0.0000 -1.0000 -0.0000
Columns 25 through 30
1.0000 -0.0000 -1.0000 -0.0000 1.0000 -0.0000
Columns 31 through 36
-1.0000 -0.0000 1.0000 0.0000 -1.0000 -0.0000
Columns 37 through 42
1.0000 0.0000 -1.0000 -0.0000 1.0000 0.0000
Columns 43 through 48
-1.0000 -0.0000 1.0000 0.0000 -1.0000 0.0000
Columns 49 through 54
1.0000 0.0000 -1.0000 -0.0000 1.0000 0.0000
Columns 55 through 60
-1.0000 0.0000 1.0000 0.0000 -1.0000 -0.0000
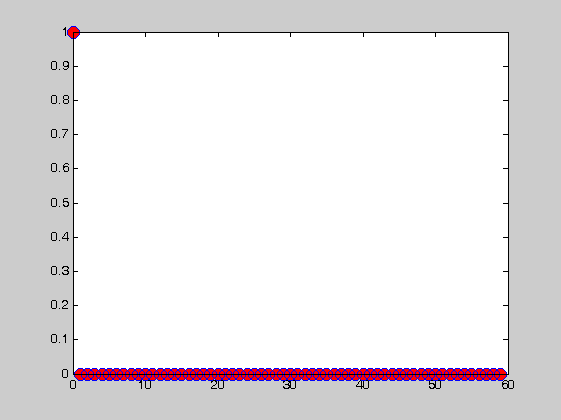
Delta function
figure(2) delta=[1 zeros(1,N-1)]; stem(n,delta,'markersize',10,'markerfacecolor','r')
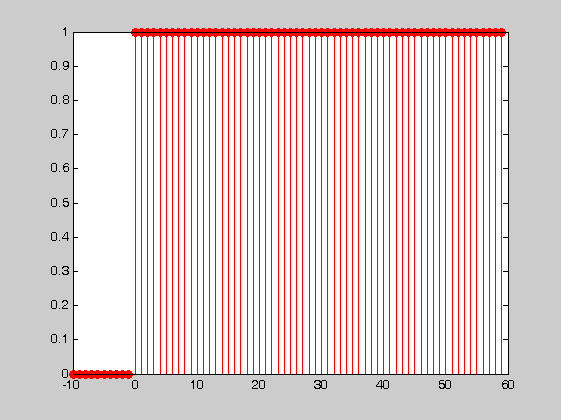
Step Function
figure(3) % In this case we show some negative time n=-10:N-1; % Set up the sample vector starting at n=-4 goint to n=N-1 (= 59) unitstep=[zeros(1,10) ones(1,N)]; stem(n,unitstep,'r','markerfacecolor','r')
Unit exponential
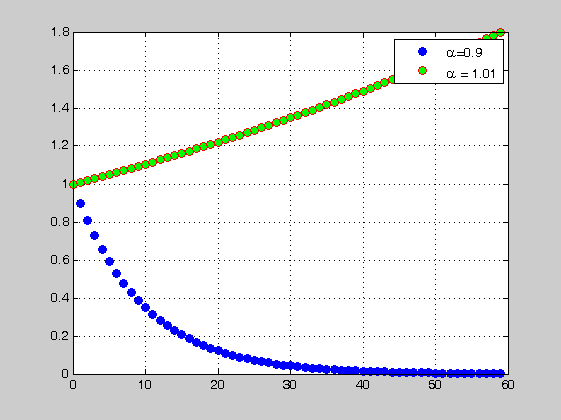
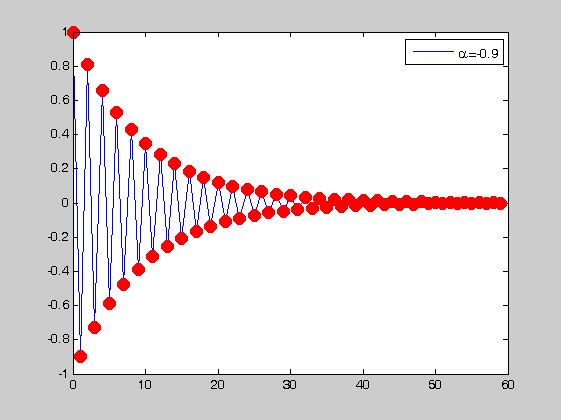
figure(4) n=0:N-1; alpha=.9; y=alpha.^n; plot(n,y,'ob','markersize',6,'markerfacecolor','b') hold on grid on alpha=1.01; y=alpha.^n; plot(n,y,'or','markersize',6,'markerfacecolor','g') legend('\alpha=0.9','\alpha = 1.01') figure(5) alpha=-.9; y=alpha.^n; plot(n,y,'or','markersize',10,'markerfacecolor','r') plot(n,y,n,y,'or','markersize',10,'markerfacecolor','r') legend('\alpha=-0.9')